Our glossary of botanical and plant-related terms for home gardeners and houseplant enthusiasts, with photos illustrating each definition.
Click on any letter below to jump right to that section of the glossary.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A

Acidic soil
Soil with a pH below 7 is considered to be acidic. Most garden and houseplants thrive at a pH between 6 and 7.5. Some plants like azaleas (pictured) love more acidic soil than most other plants.

Adventitious Root
Roots that develop after an injury to plant tissue. These include roots formed on leaf and stem cuttings, or from air layering. Some tropical trees, like ficus, produce adventitious aerial roots from their branches.

Aerial/Air Root
Roots that grow on parts of a plant above the ground. Air roots absorb moisture and nutrients. On some plants, aerial roots also serve as anchors, helping affix the plant to supporting structures.

Air Layering
A method of plant propagation using sphagnum moss. This process also occurs naturally with some plants, when a low-hanging branch or stem touches the ground and takes root.

Alkaline
Soil with a pH above 7 is considered to be alkaline. Most garden and houseplants thrive at a pH between 6 and 7.5. Alkaline soil is less soluble, so it can lead to nutrient deficiency and stunted growth.
Some plants like clematis (pictured) prefer slightly more alkaline soil than most other plants.
Alkaline soil is sometimes referred to as “sweet soil”.

Annual
A plant that flowers and dies in one season. Annuals usually bloom all season, and some produce seeds to grow new plants in the spring.

Anther
The oval-shaped structure on the end of each stamen filament on a flower. The anther produces pollen for plant reproduction.

Areole
Small fuzzy bumps on cactus plants, out of which grow flowers, stems, or clusters of spines.

Aroid
Plants from the family Araceae. Aroids are monocotyledonous flowering plants whose flowers are on a spadix.
This family includes many popular houseplants including aglaonemas, monsteras, philodendrons, pothos, and ZZ plants.

Arum
A genus of tuberous perennial plants in the family Araceae, order Arales.
Arums feature arrow-shaped leaves and a flower-like combination of spathe and spadix.
B

Biennial
a plant that grows leaves, stems, and roots the first year, then goes dormant for the winter. During the second year, the plant flowers and produces seeds before dying. Sweet william is an example of a biennial.

Bonsai
A Japanese art form for cultivating ornamental trees or shrubs in containers. Using specialized techniques, bonsai trees are prevented from reaching normal size. However, bonsai retain the shape and scale of full-sized trees.

Bract
A modified or specialized leaflike structure, usually associated with reproduction. The red anthurium bract pictured surrounds the spadix where the flowers grow.

Bud
A compact growth on a plant that develops into a leaf, shoot, or flower. The cosmos bud pictured will eventually open up into a flower.

Bulb
A globe-shaped fleshy bud that forms underground as the resting stage for some seed plants, especially perennial monocotyledons.

C
Cachepot
An ornamental holder for a flowerpot, often without a drainage hole. Used to hide a less-aesthetically-pleasing pot with better drainage.

Callus
Soft tissue that forms over a cut or wound on a plant. After callus tissue forms, some cells may become points for new growth of roots, stems, or leaves.
Formation of a callus is recommended before propagation of many succulents.

Calyx
A collection of sepals, the green covers that protect a flower bud and its reproductive organs. The calyx is an essential structure that protects the flower to help it produce new plants.

Caudex
A thickened base of some woody plants, especially palms or tree ferns. This underground structure can contribute new leaves and flowering stems to a plant.
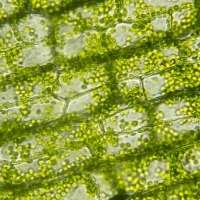
Chlorophyll
A green pigment in plants that’s responsible for absorbing light for photosynthesis.
Plants use both chlorophyll and light to make food.

Chlorosis
A negative condition in which the leaves of a plant produce insufficient chlorophyll. Chlorotic leaves often look pale yellow, yellow, or yellowish-white.

Coir
A natural fiber extracted from the outer husk of the coconut plant. This tough fiber is often used to make floor mats, brushes, and mattresses.
Coir is also used to provide a natural substrate for plants.

Corm
A flat, rounded storage organ consisting of a swollen stem base covered with scale leaves.
Examples of plants that produce corms are crocuses, gladioli, and cyclamens.

Cotyledon
The embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants. One or more cotyledons are the first leaves to sprout from a seed.

Crown
The part of a plant where the stem meets the roots, where energy is transferred from the roots to the stem. Also called the plant base.
D

Deadhead
To remove spent flowers from a plant. Removing dead and dying blooms often promotes the growth of new flowers.

Deciduous
A plant that sheds its foliage seasonally, usually in the autumn at the end of its growing season.

Distilled water
Water that has been boiled and condensed back into liquid in a separate vessel to remove impurities. Many container plants can benefit from watering with this purified water.

Dormant
The period in a plant’s growth cycle where growth is temporarily stopped. Dormancy allows many plants to survive in cold or dry seasons.
E

Emersed plant
A plant that grows partially in and partially out of water. The roots and substrate are underwater, but the stems and leaves are exposed to the air.
Etiolation

The result of a plant growing in complete or partial absence of light. Etiolated plants may have leggy, weak stems, smaller leaves, and show signs of chlorosis.
F

Frond
The leaf or a leaflike part of a palm or fern plant.

Fruit
The ripened ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. Fruit protects the seeds of a plant and is responsible for dispersing them to make new plants.
G

Glochid
Short prickles or hair-like spines, found on cacti in the sub-family Opuntioideae. Glochids grow from the plant’s areoles.

Guttation
A plant’s process of exuding drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves. Guttation occurs in some vascular plants such as grasses, and generally happens at night.
H

Honeydew
A sticky liquid secreted by aphids and other plant pests, including some scale insects. Some caterpillars and moths also produce honeydew.
(Image by Dmitri Don, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons)

Hygrometer
An analog or digital device that measures temperature and humidity in the air. These devices can be used near houseplants to monitor conditions in the plants’ environment.
I

Inflorescence
The reproductive area of a flowering plant that bears a flower or a cluster of flowers in a specific arrangement.

Internode
The section of a plant’s stem between the nodes. Internodes carry water, hormones, and nutrients from node to node.
J

Joint
The part of a plant stem where branches or leaves grow. Often used interchangeably with node.
L

Latex
A milky fluid found in some flowering plants, including ficus and poinsettias. Latex consists of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, oils, tannins, resins, and gums, and coagulates when exposed to air.

Leggy
A description of a plant that has grown tall and spindly. Leggy plants often produce fewer flowers and have an untidy appearance.
Plants can become leggy due to too much nitrogen in the soil, or due to etiolation.
M

Macronutrients
The nutrients that plants need in larger amounts. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.

Micronutrients
The nutrients that plants need in smaller, or trace amounts. These include boron, chlorine, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, and molybdenum.

Monocotyledonous
Plants with seeds that contain just one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. Examples are grasses and many grass-like flowering plants.

Monopodial
A vascular plant that grows upward from a single point.
N
Needles

The pointed, needle-shaped secondary leaves of conifer plants.
Neem oil

A naturally-occurring pesticide produced from the seeds of the neem tree. The oil is yellow or brown, and has a garlic or sulfur smell.
Neem oil can be applied to the soil, or mixed with water and sprayed on the underside of leaves to prevent pests.

Native plant
A plant that occurs naturally in a region or ecosystem without human introduction.

Node
The joints on a plant where leaves, branches, or aerial roots grow from its stem.

Non-native plant
A plant that has been introduced to an area from another region or country. Many non-native plant species don’t pose a problem to the ecosystem, while others are considered invasive, such as kudzu in the southeastern US.
O

Oedema (Edema)
A disorder that occurs when roots take up water faster than it can be used by the plant. Water pressure builds up in leaf cells until they burst, resulting in blisters on the underside of leaves.

Offset
A small daughter plant asexually produced on the mother plant. These small plants are clones of the mother plant.
Examples of plants that produce offsets are certain onions, date palm, banana, and pineapple. Offsets are often used in propagation to create new plants.

Orchid Bark
A substrate, often used to grow orchids, made from the bark of coniferous trees. Orchid bark provides greater aeration for roots than potting soil. Orchid bark can also be used as mulch for other types of plants.

Ovary
Part of the female reproductive organ of a flowering plant. The ovary is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s). This organ is located above, below, or at the connection point with the base of the petals and sepals.

GET A FREE PLANT CARE TRACKER!
Sign up for the Leafy Little Home newsletter, where we share plant tips and inspiration to turn your space into a green oasis. Plus, we'll send you a handy printable Plant Care Tracker, absolutely free!
By signing up you agree to receive the Leafy Little Home newsletter. Unsubscribe at any time.
P

Peat Moss
A moss used as a soil amendment to improve aeration. The term peat moss is often used interchangeably with sphagnum moss, although it generally has a more acidic pH level. Also used in air layering.

Pedicel
The structure that connects a single flower to its inflorescence.

Peduncle
A flower stalk that supports either a single flower or a cluster of flowers.

Perennial
A plant that lives for many growing seasons. The top portion of the plant generally dies back in winter, regrowing in spring from the same root system. Some perennials keep their leaves year-round.

Perlite
A soil amendment made from a form of obsidian. Perlite is used in soil to improve aeration and drainage.

Plant pest
An organism that is commonly injurious to plants. The term plant pest is usually applied to insect micropredators such as aphids.

Petiole
The stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem. The petiole is able to twist the leaf to face a light source.

Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants use sunlight to synthesize CO2 and water. Plants use chlorophyll in the process, and generate oxygen as a byproduct.

Phototropism
The tendency for a plant to orient itself toward a light source.

Plantlet
Small clones that are produced on the leaf edges or aerial stems of a plant.
Plantlets can be used in propagation to make new plants.

Pot bound
The condition caused when a plant’s roots fill its container, leaving no room for expansion. Also known as root bound.

Propagation
The process of growing new plants from a variety of sources. Propagation can occur from seeds, cuttings, air layering, or planting offsets or plantlets.

Pseudobulb
A thick, bulblike plant stem located above ground. Many orchids produce pseudobulbs, which are used as storage organs.

Pumice
A soil amendment made from lightweight volcanic rock. Adding pumice to potting soil helps with drainage and air circulation, while reducing water runoff.

Purified water
Water, such as distilled water, that has been processed or filtered to remove chemicals and impurities. Many plants benefit from watering with purified water.
R

Ray flower
The petals surrounding a disk of florets in some composite plants, such as the daisy.

Rhizome
A subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes tend to grow horizontally, extending from the main root of the plant. Plants that create rhizomes include bamboo, ginger, ferns, and irises.

Roots
The part of the plant, generally underground, that absorbs water and dissolved minerals to send to the stems. Roots also anchor the plant and store reserve nutrients.

Rosette
An arrangement of leaves or leaf-like structures in a concentric circular pattern.
Rosettes are formed close to the soil in plants with internodes that don’t expand, causing the leaves to cluster tightly.

Runner
Stemlike structures, each containing a tiny new plant, that extend from a mother plant. Often used interchangeably with the term stolon, although runners do not have substantial leaves.
S

Sepal
The part of a flower, usually green in color, that functions as protection for a flower bud, as well as support for the petals when in bloom.

Soil Amendment
A material added to soil to improve its properties and provide a better environment for roots.
Examples include perlite, pumice, and sphagnum moss. Soil amendments must be thoroughly mixed into the soil to work properly.

Spadix
A spike of tiny flowers on a fleshy axis. A spadix is often enclosed in or surrounded by a spathe.
Arums, like anthuriums and peace lilies, have spadices.

Spathe
A large bract that encloses the flowers of certain plants. Arums and palms have a spathe around each spadix.

Sphagnum moss
A natural moss used as a soil amendment to retain moisture and nutrients. Sphagnum moss is also used in air layering.
The term is often used interchangeably with peat moss, but peat moss has a more acidic pH level.

Stamen
The male, pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Each stamen consists of a tubelike filament and an anther.

Stem
One of the two main structural portions of a plant, along with the roots.
The stem physically supports the leaves, flowers, and fruit. It also stores and transports water and nutrients, and produces new tissue.

Stolon
A horizontal plant stem that is sent out from the mother plant. A stolon takes root to form new plants. Often used interchangeably with runner.

Submersed plant
A plant that grows completely or almost completely underwater. When submersed plants have flowers, they may be above the water’s surface.

Succulent
A type of plant with thickened, engorged flesh. Succulents retain water in arid climates and dry soil conditions. Examples include cactus, aloe vera, and jade plants.

Sympodial
A type of plant that grows multiple upright stems from a horizontal stem.
Some orchids are sympodial, with several pseudobulbs growing from a rhizome.
T

Terrestrial plants
Any plant that grows on, in, or from land.
Other types of plants include aquatic plants, lithophytic plants (living on rocks) and epiphytic plants (living on trees).

Thorn
A sharp, stiff, woody projection on the stem or other part of a plant. Thorns can be straight or curved.

Tissue Culture
A type of plant propagation where cells, tissues, or organs are grown under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium.
Tissue culture produces clones of the original mother plant.

Top Dress
A layer of rich soil mix added at the crown of a plant. Top dress contains organic matter to provide nutrients to the plant.

Transpiration
The loss of water vapor from a plant via small pores in the leaves.

Trichomes
Small hairs or growths from the epidermis of a plant. Trichomes help protect a plant from temperature extremes or plant pests.

Tuber
A thickened, underground stem or rhizome that stores nutrients and creates new plants.
U

Umbel
A flower cluster with rays of nearly equal length, forming a flat or curved surface. Examples include parsley and Queen Anne’s lace.
V

Variegated
The appearance of different colored zones on the leaves and sometimes stems of a plant.
Variegation occurs because of a lack of chlorophyll in some of the cells, and is usually caused by a cell mutation.

Vermiculite
A yellow or brown mineral soil amendment produced from mica. Vermiculite is used for insulation and to retain moisture.
W

Weed
A plant that is not considered valuable and tends to choke or overgrow more desired plants.
Pin this to save for later!






